Introduction
Laparoscopic diaphragmatic hernia repair is a modern, minimally invasive surgery. It helps fix a hole or weakness in the diaphragm. This procedure is important because it can relieve symptoms and prevent serious health problems. Many people choose this method because it often leads to a faster recovery and less pain. In this guide, you will learn what a diaphragmatic hernia is, how the surgery works, and what to expect during recovery. Understanding your options can help you make the best choice for your health.
What is a Diaphragmatic Hernia?
A diaphragmatic hernia happens when an organ, like the stomach, moves through a weak spot in the diaphragm. The diaphragm is a muscle that separates the chest from the belly. Normally, it helps you breathe. However, a hernia can let organs push into the chest area. This can cause discomfort and other health issues. There are different types of diaphragmatic hernias, such as congenital (present at birth) and acquired (develop later in life). Each type may need a different treatment approach.
What is Laparoscopic Diaphragmatic Hernia Repair?
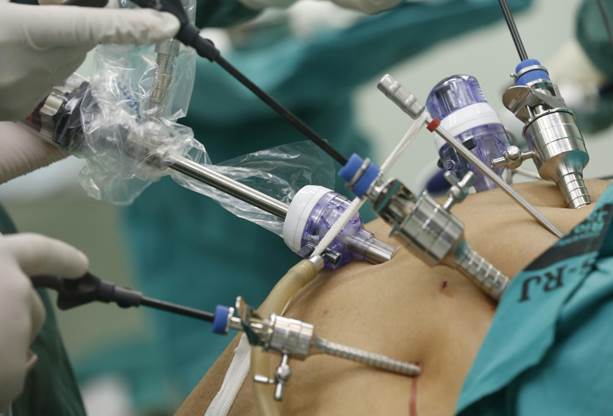
Laparoscopic diaphragmatic hernia repair is a type of minimally invasive hernia surgery. Instead of making a large cut, the surgeon uses small incisions and special tools. A tiny camera, called a laparoscope, helps the surgeon see inside the body. As a result, this method often causes less pain and allows for a quicker recovery. Many hospitals in the United States and around the world now use this advanced technique. It is considered safe and effective for most patients.
Symptoms and Causes of Diaphragmatic Hernia
People with a diaphragmatic hernia may notice different symptoms. Some common signs include:
Shortness of breath
Chest pain or discomfort
Heartburn or acid reflux
Feeling full quickly after eating
Vomiting or nausea
However, some people may not have any symptoms at all. Causes of diaphragmatic hernia can include birth defects, injury, or increased pressure in the belly. For example, heavy lifting, obesity, or chronic coughing can raise the risk. Understanding the causes can help with prevention and early treatment.
Diagnosis Process
Doctors use several steps to diagnose a diaphragmatic hernia. First, they ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they may do a physical exam. Often, imaging tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include:
Chest X-ray
CT scan
MRI scan
Upper GI series (a special X-ray with contrast dye)
With these tools, doctors can see the hernia and plan the best treatment. Early diagnosis is important for better outcomes.
Step-by-Step Surgical Procedure
Laparoscopic diaphragmatic hernia repair follows several steps. Here is what usually happens:
First, the patient receives anesthesia to sleep during surgery.
Next, the surgeon makes a few small cuts in the belly.
Then, a laparoscope and other tools are inserted through these cuts.
The surgeon gently moves the organs back into place.
After that, the weak spot in the diaphragm is repaired, often with stitches or a mesh patch.
Finally, the tools are removed and the cuts are closed.
This whole process usually takes one to two hours. Most patients go home the same day or after a short hospital stay.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery offers many advantages over open surgery. Some key benefits include:
Smaller incisions and less scarring
Less pain after surgery
Shorter hospital stay
Faster return to normal activities
Lower risk of infection
Because of these benefits, many patients and doctors prefer this minimally invasive hernia surgery. According to the CDC and recent studies, recovery after hernia repair is often smoother with this method.
Risks and Possible Complications
Although laparoscopic diaphragmatic hernia repair is safe, every surgery has risks. Possible complications may include:
Bleeding or infection
Injury to nearby organs
Hernia coming back (recurrence)
Problems with anesthesia
However, most people recover without serious problems. Your surgeon will discuss these risks before the procedure. It is important to follow all instructions to lower your risk.
Recovery and Aftercare Tips
After surgery, recovery is usually quick. Most people feel better within a few days. To help your healing, follow these tips:
Rest as much as needed, but try gentle walking
Take pain medicine as directed
Eat small, light meals at first
Avoid heavy lifting for a few weeks
Keep the incision area clean and dry
Watch for signs of infection, like redness or fever
Always attend follow-up visits with your doctor. If you notice severe pain, trouble breathing, or other concerns, contact your healthcare provider right away.
Prevention and Lifestyle Guidance
While not all hernias can be prevented, some steps may help lower your risk. Consider these healthy habits:
Maintain a healthy weight
Avoid heavy lifting or use proper technique
Treat chronic coughs or constipation
Eat a balanced diet to support muscle strength
Stop smoking, as it can weaken muscles
By making these changes, you can support your overall health and reduce the chance of hernia problems in the future.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic diaphragmatic hernia repair is a safe and effective way to treat hernias in the diaphragm. With its many benefits, this minimally invasive hernia surgery helps many people return to normal life quickly. If you think you may have a hernia or need advice about treatment, consult a qualified general surgeon for personalized advice on laparoscopic diaphragmatic hernia repair.